A barcode, consisting of bars and spaces, is a machine-readable representation of numerals and characters. Today, stripes as shown below on packages of products sold at supermarkets, convenience stores and other stores are ubiquitous. These are barcodes. A barcode consists of bars and spaces of varying width that can be read with an optical barcode scanner.
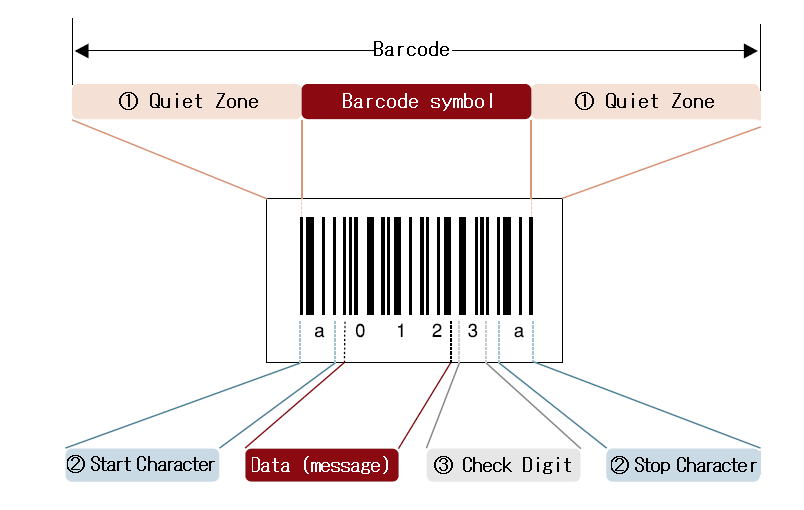
Quiet Zone is a blank margin located at either end of a barcode. The minimal margin between barcodes (distance from the outermost bar of one barcode to the outermost bar of another barcode) is 2.5 mm. If the width of a Quiet Zone is insufficient, barcodes are hard for a scanner to read.
The Start Character and the Stop Character are characters representing the start and the end of the data, respectively. The characters differ depending on the barcode type.
The Check Digit is a digit for checking whether the encoded barcode data are correct.
Common product codes are broadly divided into two groups: UPC and EAN.
In Japan, as a kind of EAN, JAN (Japanese Article Number) is used. EAN (JAN) consists of 13 digits in the standard version and 8 digits in the shortened version. UPC consists of 12 digits and 7 digits (including the check digit) in the standard and shortened versions, respectively. EAN/UPC has been standardized as an ISO standard (ISO/IEC15420) and a JIS standard (JISX0507). In Japan, JAN codes are affixed to food, sundry articles, etc. and are mainly used in Point Of Sales (POS) systems.
The composition of a common product code is common in all countries, and a country code has been assigned to each country.
For example, "49" and "45" are assigned to Japan.

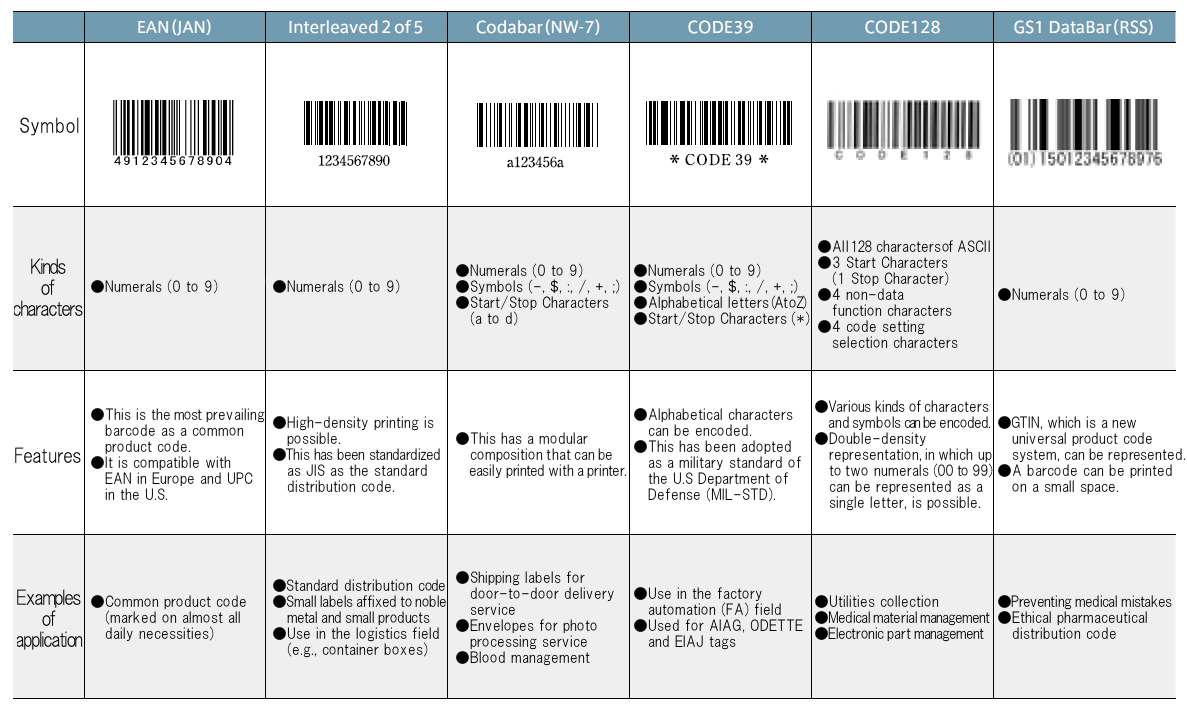
NW-7 has a modular composition that can be easily printed with a printer. It is used for shipping labels for door-to-door delivery service, envelopes for photo processing service, etc. Data that can be encoded are numerals (0 to 9) and symbols ("-", "$", ":", "/", "+" and ";"). For the Start Character and the Stop Character, A, B, C or D can be selected.

InterLeaved 2 of 5 enables high-density printing, and is used in the logistics field (e.g., container boxes) and for small labels affixed to noble metal and small products. It was standardized as a distribution product barcode symbol (JIS-X-0502) in 1987 and as JIS (JISX0505) in 2004.

CODE39 enables the representation of alphabetical characters, and has been adopted as a military standard of the U.S Department of Defense (MIL-STD). It is widely used in the factory automation (FA) field and for AIAG, ODETTE and EIAJ tags. Data that can be encoded are numerals (0 to 9), symbols ("-", " " (space), "$", "/", "+", "%" and ".") and alphabetical letters (A to Z).

CODE128 can encode all 128 characters of ASCII. It is used mainly in the factory automation (FA) and office automation (OA) fields. Data that can be encoded are all 128 characters of ASCII. It comprises three code sets.

GS1 Databar has three types of seven symbols. GS1 Databar can represent data in a smaller area than existing barcodes. By using Application Identifiers (AIs), which are standardized by the GS1 Japan, information on product attributes, including expiration dates and lot numbers, can be represented. In 2015, labeling GS1 Databar symbols on all ethical pharmaceuticals was made obligatory.











If you have not registered
The services on this member site are available only for registered customers.